các đồng chí giải hộ với 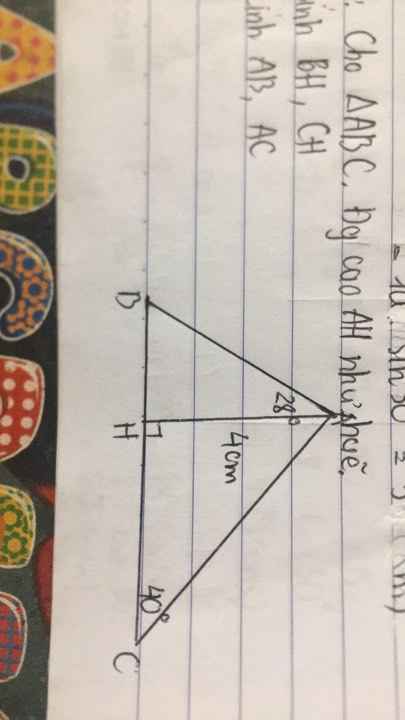
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=0\\x\ne4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(P=\left(\dfrac{2}{x-4}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\right):\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2+\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{1}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
Để P=3/2 thì \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
=>\(3\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)=2\sqrt{x}\)
=>\(3\sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}=6\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}=6\)
=>x=36(nhận)

a: 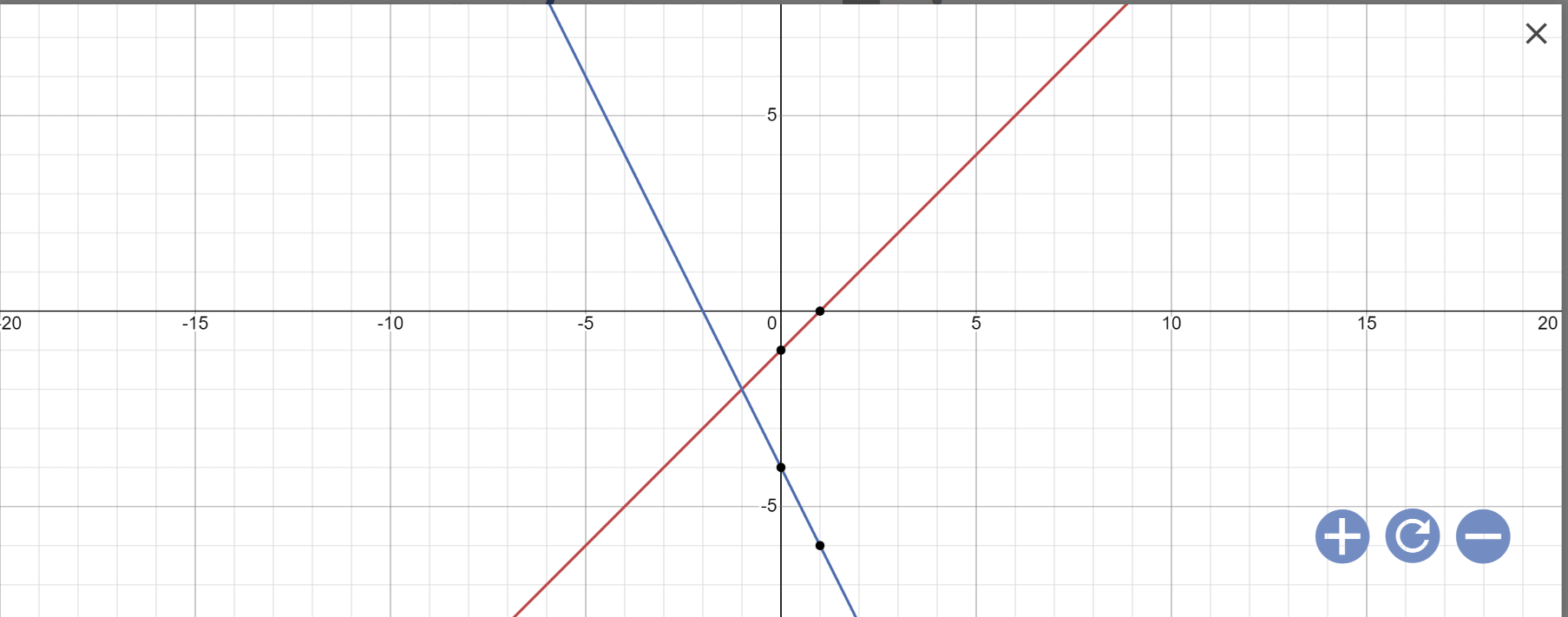
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
-2x-4=x-1
=>-2x-x=-1+4
=>-3x=3
=>x=-1
Thay x=-1 vào y=x-1, ta được:
y=-1-1=-2
Vậy: Tọa độ giao điểm là A(-1;-2)

a.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(2x-3y\right)\left(2x-y\right)=0\\6x^2+7xy-5y^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH1: \(2x-3y=0\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2}{3}x\) thay vào pt dưới
\(\Rightarrow6x^2+7x.\left(\dfrac{2}{3}x\right)-5\left(\dfrac{2}{3}x\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{76}{9}x^2=0\Rightarrow x=0\Rightarrow y=0\)
TH2: \(2x-y=0\Rightarrow y=2x\)
Tương tự ta cũng được \(x=0;y=0\)
Vậy hệ có nghiệm duy nhất \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(0;0\right)\)
b.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}13x^2-39xy+13y^2=-13\\2x^2+xy+3y^2=13\end{matrix}\right.\)
Cộng vế với vế
\(\Rightarrow15x^2-38xy+16y^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2y\right)\left(15x-8y\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2y\\x=\dfrac{8}{15}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay vào pt đầu:
- Với \(x=2y\Rightarrow4y^2-6y^2+y^2=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow y^2=1\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=1\Rightarrow x=2\\y=-1\Rightarrow x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Với \(x=\dfrac{8}{15}y\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\dfrac{8}{15}y\right)^2-3\left(\dfrac{8}{15}y\right).y+y^2=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{71}{225}y^2=-1\Rightarrow y^2=\dfrac{225}{71}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{71}}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{71}}\\y=-\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{71}}\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{71}}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có \(sinB=\dfrac{AC}{BC}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6}{BC}=sin30=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>\(BC=6\cdot2=12\left(cm\right)\)

\(\left|A+B\right|< =\left|A\right|+\left|B\right|\)
=>\(\left(\left|A+B\right|\right)^2< =\left(\left|A\right|+\left|B\right|\right)^2\)
=>\(A^2+B^2+2AB< =A^2+B^2+2\left|AB\right|\)
=>2AB<=2|AB|
=>AB<=|AB|(luôn đúng)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi AB>=0

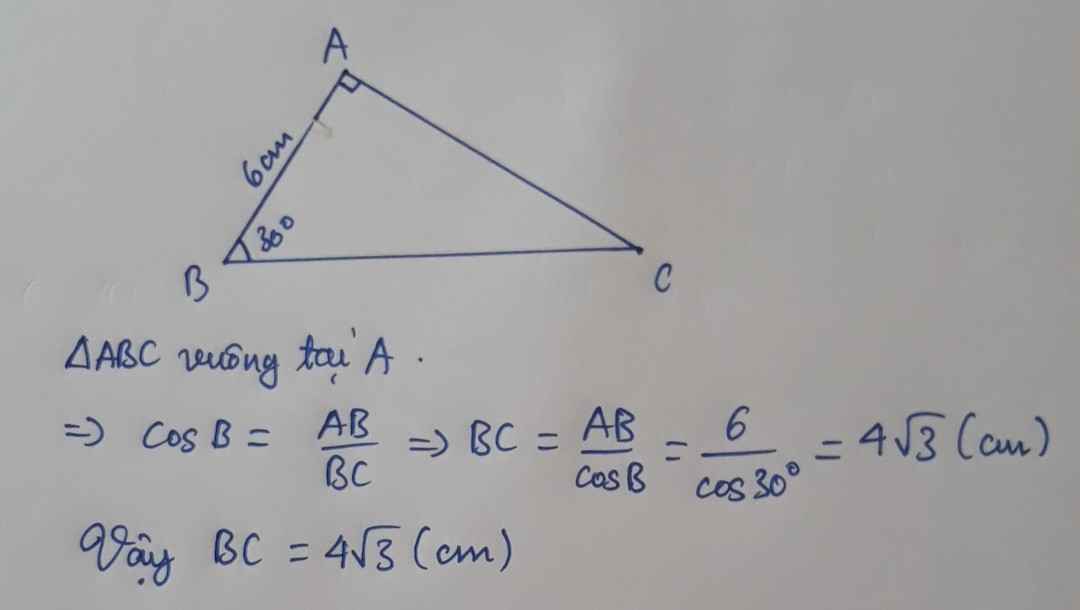
xét ΔABC vuông tại A có \(cosB=\dfrac{AB}{BC}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6}{BC}=cos30=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
=>\(BC=6\cdot\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}=4\sqrt{3}\left(cm\right)\)


a: \(\dfrac{3x+5}{2}-x>=1+\dfrac{x+2}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{3x+5-2x}{2}>=\dfrac{3+x+2}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+5}{2}-\dfrac{x+5}{3}>=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{3\left(x+5\right)-2\left(x+5\right)}{6}>=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+5}{6}>=0\)
=>x+5>=0
=>x>=-5
b: \(\dfrac{x-2}{3}-x-2< =\dfrac{x-17}{2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)}{6}+\dfrac{6\left(-x-2\right)}{6}< =\dfrac{3\left(x-17\right)}{6}\)
=>\(2\left(x-2\right)+6\left(-x-2\right)< =3\left(x-17\right)\)
=>\(2x-4-6x-12< =3x-51\)
=>-4x-16<=3x-51
=>-7x<=-35
=>x>=5
c: \(\dfrac{2x+1}{3}-\dfrac{x-4}{4}< =\dfrac{3x+1}{6}-\dfrac{x-4}{12}\)
=>\(\dfrac{4\left(2x+1\right)-3\left(x-4\right)}{12}< =\dfrac{2\left(3x+1\right)-x+4}{12}\)
=>4(2x+1)-3(x-4)<=2(3x+1)-x+4
=>8x+4-3x+12<=6x+2-x+4
=>5x+16<=5x+6
=>16<=6(sai)
Vậy: BPT vô nghiệm

a: \(\dfrac{3\left(2x+1\right)}{20}+1>\dfrac{3x+52}{10}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6x+3}{20}+\dfrac{20}{20}>\dfrac{6x+104}{20}\)
=>6x+23>6x+104
=>23>104(sai)
vậy: \(x\in\varnothing\)
b: \(\dfrac{4x-1}{2}+\dfrac{6x-19}{6}< =\dfrac{9x-11}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{3\left(4x-1\right)+6x-19}{6}< =\dfrac{2\left(9x-11\right)}{6}\)
=>12x-3+6x-19<=18x-22
=>-22<=-22(luôn đúng)
Vậy: \(x\in R\)
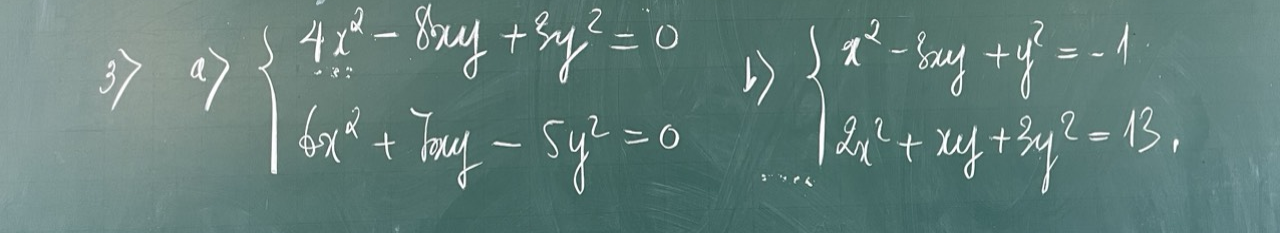
Xét ΔAHB vuông tại H có \(tanBAH=\dfrac{BH}{AH}\)
=>\(BH=AH\cdot tanBAH=4\cdot tan28\simeq2,13\left(cm\right)\)
Xét ΔAHC vuông tại H có
\(tanC=\dfrac{AH}{HC}\)
=>\(HC=\dfrac{AH}{tanC}=\dfrac{4}{tan40}\simeq4,77\left(cm\right)\)
ΔAHB vuông tại H
=>\(AH^2+HB^2=AB^2\)
=>\(AB=\sqrt{AH^2+HB^2}\simeq4,53\left(cm\right)\)
ΔAHC vuông tại H
=>\(AH^2+HC^2+AC^2\)
=>\(AC=\sqrt{AH^2+HC^2}\simeq6,23\left(cm\right)\)